IP Settings (for Connect ES 4/8 SB with Ethernet switch only)
This section describes configuring and deploying Digi Connect ES4/8 SB with Switch devices in a network.
The Digi Connect ES4/8 SB with Switch has two Ethernet interfaces:
-
Ethernet Uplink: An uplink interface that connects to the central data management system network.
The uplink interface provides a single Internet Protocol (IP) address for all communication to and from the devices at a single location. Network Address Translation (NAT) and port forwarding provide seamless network access through the Digi Connect ES SB SW for all Ethernet and serial devices at that location. DHCP or static addresses are used for IP address assignment of the uplink interface.
-
Ethernet Switch: A four-port switch that creates a Local Area Network (LAN).
The LAN switch provides network connectivity for up to four network devices, in addition to the Digi Connect ES SB SW which provides four or eight isolated RS‑232 serial ports. The default IP address for the LAN interface of the Digi Connect ES 4/8 SB with Switch is 192.168.1.1. The other network devices connected to the Digi Connect ES 4/8 SB with Switch share this same Class C network address scheme (192.168.1.x). A Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server is provided on this interface to allow dynamic assignment of devices as well.
The following figure shows the location of the Ethernet Uplink and Switch ports on the product:
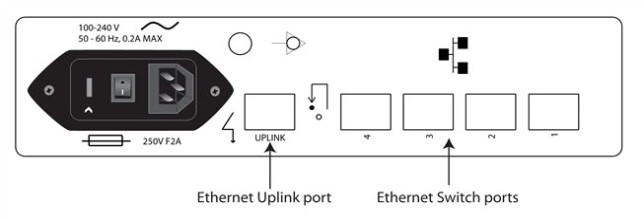
Because the LANs attached to each Digi Connect ES 4/8 SB with Switch are typically not connected to each other, equipment can have static network addresses and be moved from one location to another without needing to be reconfigured. The central data management system can easily communicate with the equipment by addressing the appropriate Digi Connect ES 4/8 SB with Switch device. The Digi Connect ES 4/8 SB with Switch uses NAT and port forwarding to make the connection.
See Configure the Ethernet interface for Connect ES 4/8 SB with Switch for instructions on configuring the network topology just described.
 PDF
PDF


